Finding a reliable source for Geotechnical Engineering Principles And Practices 2nd Edition Pdf Free Download can be challenging. This comprehensive guide aims to provide valuable insights into the subject while addressing the common queries students and professionals may have.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Key Principles of Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering, a branch of civil engineering, focuses on the behavior of earth materials. Understanding soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and groundwater hydrology is crucial for designing safe and sustainable infrastructures.
Soil Mechanics: The Foundation of Geotechnical Engineering
Soil mechanics deals with the physical properties of soil and how it interacts with structures. Key concepts include:
- Soil Classification: Categorizing soils based on their properties like grain size, consistency, and plasticity.
- Shear Strength: Determining the soil’s resistance to deformation under stress, crucial for foundation design.
- Consolidation: Analyzing how soil compresses over time due to external loads, impacting settlement of structures.
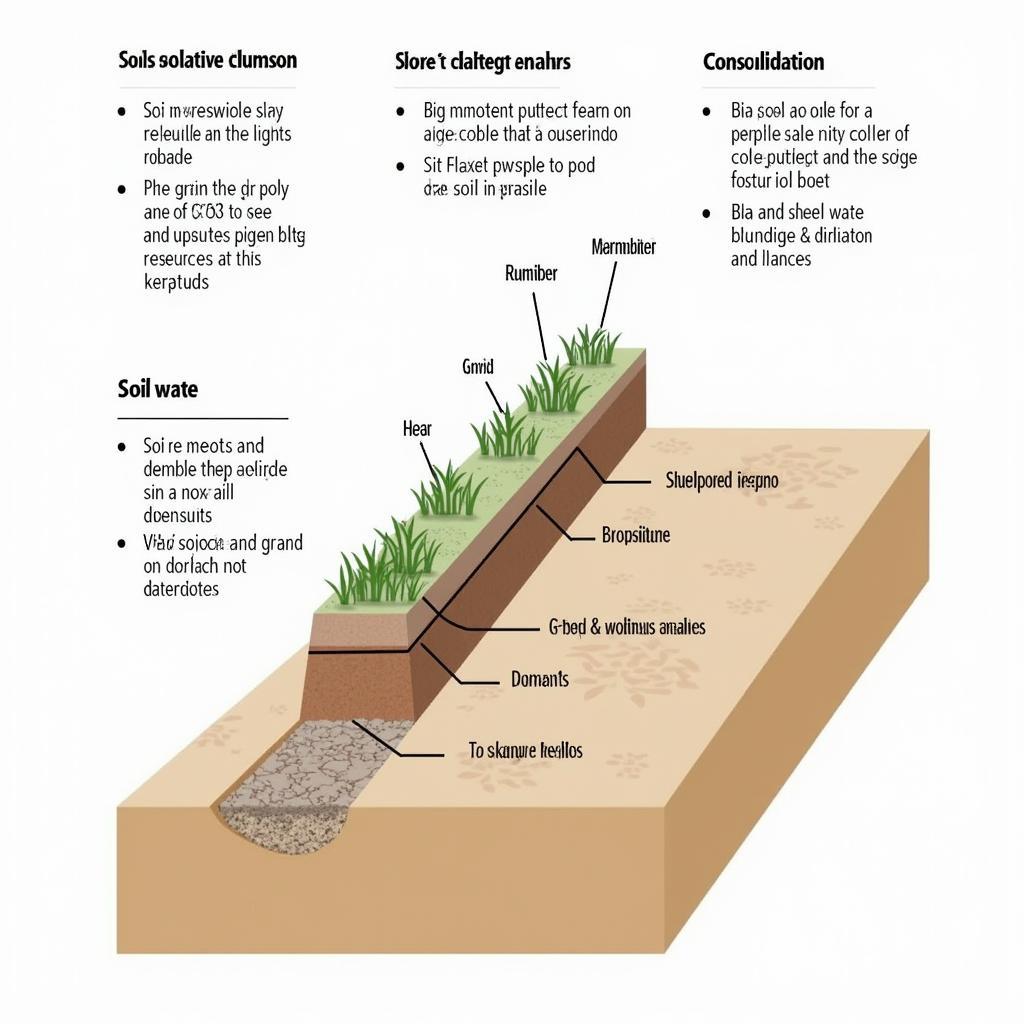 Soil Mechanics Principles
Soil Mechanics Principles
Rock Mechanics: Engineering in Solid Ground
Rock mechanics examines the behavior of rocks under different stress conditions. This field is vital for projects involving:
- Tunneling: Understanding rock mass behavior for safe tunnel excavation and support design.
- Slope Stability: Analyzing the stability of rock slopes to prevent landslides and ensure safety.
- Foundations on Rock: Designing foundations for structures built on rock, considering rock strength and deformation characteristics.
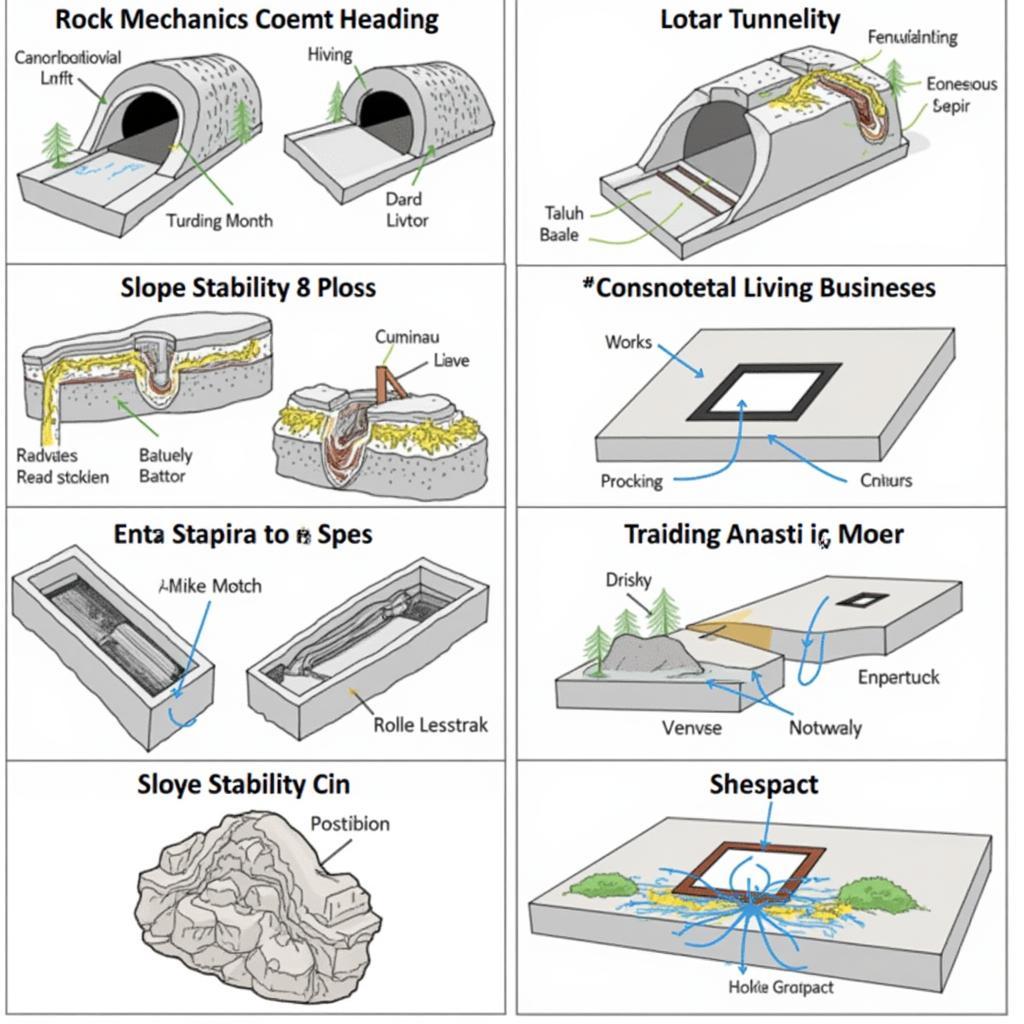 Rock Mechanics Applications
Rock Mechanics Applications
Groundwater Hydrology: The Invisible Force
Groundwater hydrology explores the movement and distribution of groundwater. Its importance in geotechnical engineering lies in:
- Seepage Control: Managing groundwater flow to prevent issues like uplift pressure on dams and erosion beneath structures.
- Groundwater Contamination: Assessing and mitigating the risk of groundwater contamination from various sources.
- Dewatering: Temporarily removing groundwater during construction to provide stable working conditions.
Putting Principles into Practice: Applications of Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineering principles are applied in various real-world scenarios, ensuring the stability and longevity of structures. Some key applications include:
- Foundation Design: Selecting appropriate foundation types (shallow or deep) based on soil properties and load-bearing capacity.
- Earth Retaining Structures: Designing retaining walls, sheet piles, and other structures to support soil and prevent slope failures.
- Ground Improvement Techniques: Implementing methods like compaction, grouting, and soil reinforcement to enhance soil properties for construction.
- Earthquake Engineering: Analyzing soil behavior during seismic events and designing earthquake-resistant structures.
Conclusion
Understanding geotechnical engineering principles and practices is paramount for constructing safe, reliable, and sustainable infrastructures. This guide provides a starting point for further exploration of this fascinating field.
Remember: When working on geotechnical projects, always consult reputable resources and seek expert advice for specific design considerations.