Edge computing has emerged as a transformative technology, extending cloud capabilities closer to data sources and end-users. For solution architects, understanding edge computing patterns is crucial for designing efficient, scalable, and responsive applications. This article delves into the world of edge computing patterns, providing valuable insights and resources, including a free downloadable PDF guide.
Understanding Edge Computing and Its Importance
Before we explore the various patterns, let’s establish a clear understanding of edge computing. In essence, edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the devices and users that generate and consume them. This proximity offers several advantages over traditional centralized cloud models, such as:
-
Reduced Latency: Processing data closer to its source minimizes network latency, resulting in faster response times and improved user experiences. This is especially critical for real-time applications like industrial automation, online gaming, and autonomous vehicles.
-
Increased Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data at the edge, less information needs to be transmitted to the cloud, reducing bandwidth consumption and network congestion. This efficiency becomes increasingly important as the volume of data generated by IoT devices continues to grow exponentially.
-
Enhanced Security and Privacy: Edge computing enables localized data processing and storage, reducing the amount of sensitive information transmitted and stored in the cloud. This distributed approach enhances security and privacy, addressing concerns related to data breaches and unauthorized access.
-
Improved Resilience and Reliability: By distributing computing resources closer to users, edge computing reduces reliance on a single centralized cloud infrastructure. This distributed nature enhances resilience to outages and ensures greater reliability for critical applications.
Key Edge Computing Patterns for Solution Architects
Solution architects play a vital role in designing and implementing effective edge computing solutions. To address the diverse requirements of modern applications, several edge computing patterns have emerged, each offering unique benefits and addressing specific use cases. Let’s explore some of the most prominent patterns:
1. Device Edge
The Device Edge pattern focuses on deploying computing resources directly on or near individual devices. This pattern is ideal for applications requiring ultra-low latency and real-time processing, such as:
-
Industrial IoT: Sensors and actuators in manufacturing environments require immediate data processing and response times to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
-
Healthcare Monitoring: Wearable devices and medical equipment generate time-sensitive data that needs to be analyzed locally for real-time diagnosis and treatment adjustments.
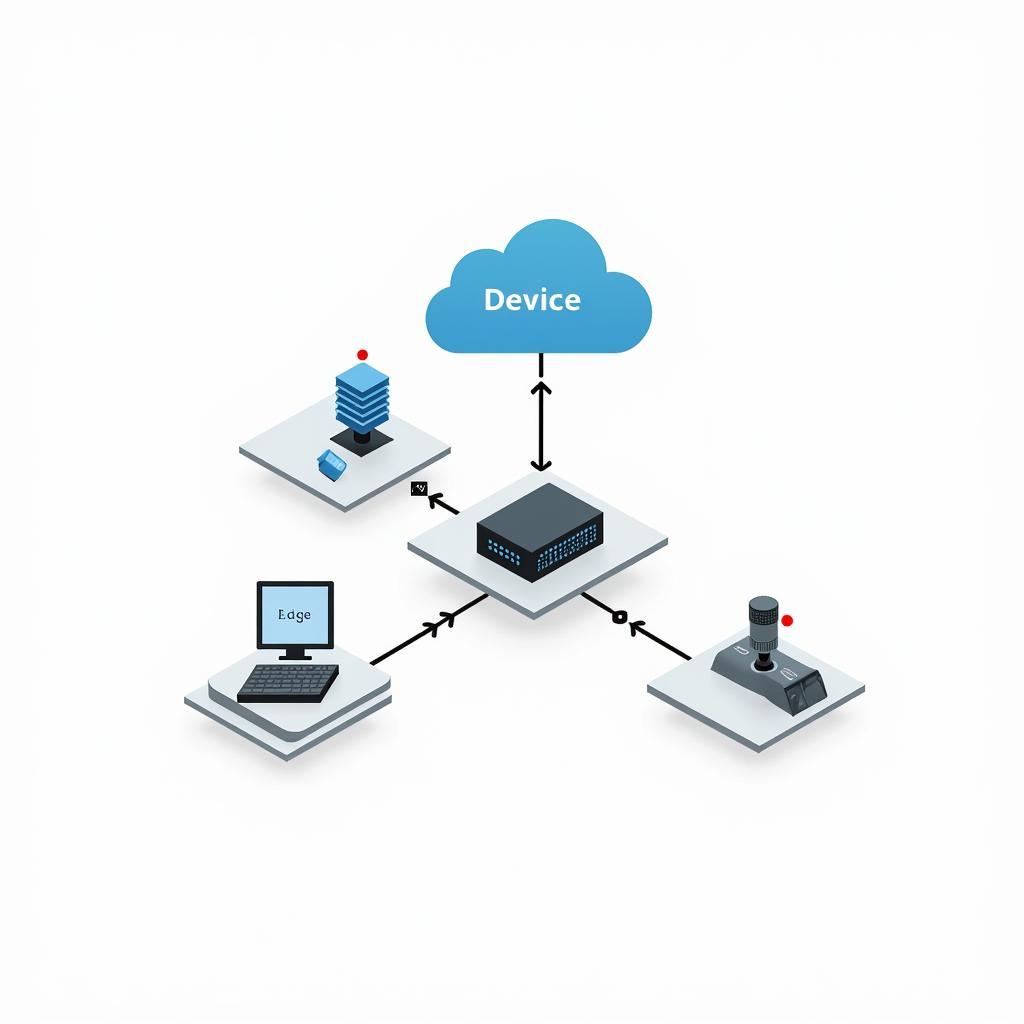 Device Edge Pattern
Device Edge Pattern
2. Gateway Edge
The Gateway Edge pattern utilizes intermediary gateways to aggregate data from multiple devices and perform initial processing before transmitting it to the cloud. This pattern is well-suited for applications that benefit from local data filtering, aggregation, and analysis, including:
-
Smart Cities: Edge gateways deployed in traffic lights, streetlights, and environmental sensors can collect and analyze real-time data to optimize traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance public safety.
-
Retail Analytics: Sensors in retail stores can track customer movement patterns, inventory levels, and environmental conditions. Edge gateways can analyze this data locally to provide real-time insights for optimizing store layouts, inventory management, and customer experiences.
 Gateway Edge Pattern
Gateway Edge Pattern
3. Cloud Edge
The Cloud Edge pattern extends cloud services closer to users by deploying edge data centers and computing resources at the network edge. This pattern offers the benefits of cloud computing with reduced latency and improved performance for applications like:
-
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs leverage edge data centers to cache and deliver content closer to users, reducing latency and improving streaming and download speeds.
-
Gaming: Edge computing enables game developers to host game servers closer to players, minimizing lag and providing a more responsive and enjoyable gaming experience.
Conclusion
As the volume and velocity of data continue to grow, edge computing has become an essential paradigm for building modern, responsive, and efficient applications. Understanding the various edge computing patterns empowers solution architects to design and deploy solutions that optimize performance, security, and scalability. By leveraging the power of edge computing, organizations can unlock new possibilities and deliver exceptional user experiences.
To further enhance your understanding of edge computing patterns, we encourage you to download our comprehensive PDF guide, “Edge Computing Patterns for Solution Architects.” This free resource provides in-depth insights, practical examples, and best practices to guide you in your edge computing journey.